Introduction
Birth control pills, also known as oral contraceptives, are one of the most widely used methods of contraception among women in India. They are effective, affordable, and easily available in pharmacies. However, many women worry about the long-term effects of birth control pills on health. Concerns such as weight gain, mood changes, and risks like blood clots or hormonal imbalances are often raised. In this blog, we’ll explain the impact of prolonged pill use, what science says, and when to see a general physician for guidance.
Understanding Birth Control Pills
Birth control pills contain synthetic hormones (estrogen and/or progestin) that prevent pregnancy by:
- Stopping ovulation
- Thickening cervical mucus to block sperm
- Thinning the uterine lining to prevent implantation
They are usually taken daily for long-term contraception.
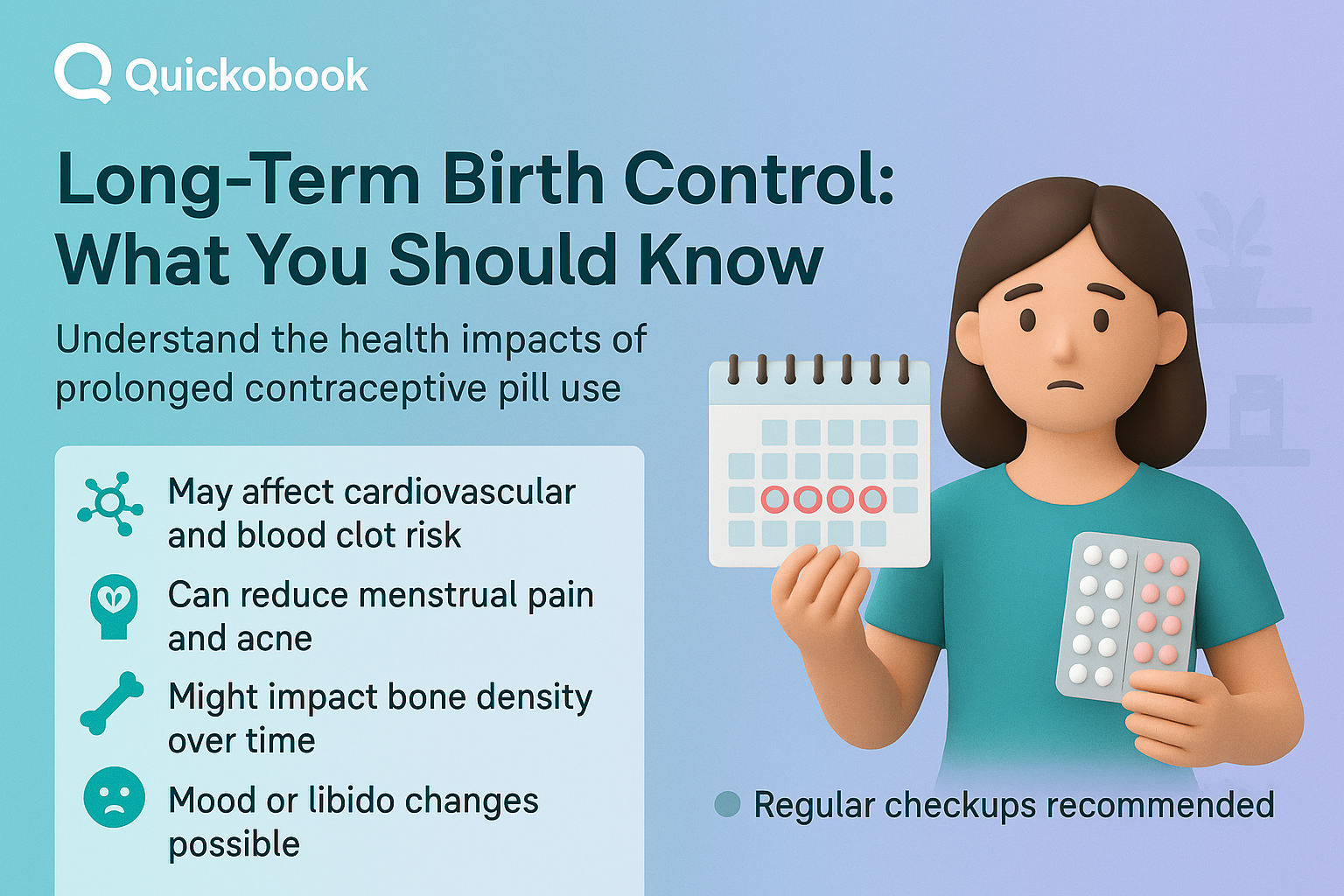
Common Effects of Long-Term Pill Use
1. Weight Gain
One of the most common worries is weight gain. While some women experience mild fluid retention or increased appetite, scientific studies show that significant weight gain is not inevitable. Lifestyle factors like diet and exercise play a major role.
2. Menstrual Cycle Regulation
- Many women notice lighter, regular, and less painful periods.
- Reduced risk of anemia due to lighter bleeding.
3. Fertility
- Fertility usually returns within a few months after stopping the pill.
- Long-term use does not cause permanent infertility.
4. Skin and Hair
- Pills can reduce acne and excess hair growth in some women.
- Rarely, they may cause hair thinning.
Potential Risks of Long-Term Use
1. Blood Clots
Prolonged use can increase the risk of blood clots, especially in women who smoke, are overweight, or have a family history.
2. Cancer Risks
- Reduced risk: Ovarian and endometrial cancer.
- Slightly increased risk: Breast and cervical cancer (which decreases after stopping).
3. Bone Health
Some studies suggest possible effects on bone density, particularly in younger women.
4. Mood Changes
Some women may experience mood swings or mild depression. Consultation with a general physician is important if symptoms persist.
When to See a General Physician
Consult a General physician if you experience:
- Severe headaches
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Sudden leg swelling or pain
- Unusual vaginal bleeding
- Persistent mood changes
A doctor can help adjust the pill type or suggest alternatives like IUDs, implants, or barrier methods.
Lifestyle Tips for Women on Birth Control Pills
- Maintain a balanced diet to prevent unnecessary weight gain.
- Stay active with regular exercise.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol.
- Visit a general physician for routine health check-ups.
- Buy medicines from trusted pharmacies to avoid counterfeit products.
Prevention & Safer Use
- Get annual check-ups, including blood pressure monitoring.
- Discuss family history of heart disease or cancer with your doctor.
- Don’t self-prescribe—consult a general physician before starting or changing pills.
Risks and Complications
- Cardiovascular risks for smokers and women over 35.
- Possible gallbladder issues in some users.
- Rare cases of liver problems.
Conclusion
Long-term use of birth control pills is generally safe for healthy women, with benefits such as regulated periods and reduced cancer risks. However, side effects like weight gain and rare complications require medical attention. Always consult a general physician before starting or continuing the pill. Quickobook makes it easy to book appointments and find nearby pharmacies for safe access to medicines.
50 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can birth control pills cause permanent weight gain?
A. No, most women do not experience permanent weight gain. Lifestyle factors matter more.
Q2. Do pills affect fertility long term?
A. Fertility usually returns within months of stopping the pill.
Q3. Are birth control pills safe for women over 35?
A. They can be safe, but smokers and those with health issues should consult a general physician.
Q4. Do birth control pills reduce the risk of ovarian cancer?
A. Yes, long-term use lowers the risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers.
Q5. Can pills cause depression?
A. Some women may feel mood changes; consult a doctor if it persists.
Q6. Do pills help with acne?
A. Yes, many women notice clearer skin with certain pills.
Q7. Can I buy pills directly from a pharmacy?
A. Yes, but always use them under medical guidance.
Q8. Do birth control pills stop periods completely?
A. They often lighten and regulate periods but rarely stop them fully.
Q9. Are there non-hormonal alternatives to the pill?
A. Yes, such as copper IUDs, condoms, and fertility tracking.
Q10. Can I drink alcohol while on the pill?
A. Yes, moderate alcohol does not affect effectiveness
Q11. Do pills protect against STIs?
A. No, condoms are needed to prevent infections.
Q12. Can pills cause migraines?
A. Some women may experience headaches; seek medical advice.
Q13. How long can I safely take the pill?
A. Many women use it for years under doctor supervision.
Q14. Can I skip my period with birth control pills?
A. Yes, some pill packs are designed to reduce or skip periods.
Q15. Do birth control pills cause blood clots?
A. They can slightly increase the risk, especially in smokers.
Q16. Can the pill improve PCOS symptoms?
A. Yes, it can help regulate cycles and reduce acne.
Q17. Does stopping the pill cause weight loss?
A. Not necessarily; weight depends more on diet and lifestyle.
READ ALSO: Natural Ways To Boost Sperm Quality And Count
Q18. Can I take pills after pregnancy?
A. Yes, but your doctor will guide you on the safe type.
Q19. Do birth control pills affect libido?
A. Some women notice changes, but effects vary.
Q20. Can I get pregnant while on the pill?
A. Rarely, if taken correctly, pills are over 99% effective.
Q21. Are pills safe for teenagers?
A. Yes, with medical guidance, they are safe and effective.
Q22. Can birth control pills cause cancer?
A. They lower some cancer risks but slightly increase others.
Q23. Do birth control pills affect bone strength?
A. Some studies suggest minor effects in young women.
Q24. Can I miss one pill without risk?
A. Missing one pill may reduce effectiveness; take it as soon as possible.
Q25. Do birth control pills affect thyroid levels?
A. They can influence test results but usually not thyroid function.
Q26. Can I use pills to delay my period for travel?
A. Yes, under doctor’s guidance, pills can shift cycles.
Q27. Do pills increase blood pressure?
A. Some women may develop higher blood pressure on the pill.
Q28. Can I breastfeed while taking the pill?
A. Progestin-only pills are recommended for breastfeeding women.
Q29. Do pills make periods painful?
A. No, they usually make periods lighter and less painful.
Q30. Can birth control pills cause skin pigmentation?
A. Rarely, some women notice dark patches called melasma.
Q31. Are pills reversible?
A. Yes, fertility usually returns quickly after stopping.
Q32. Can I take pills without seeing a doctor?
A. It’s safer to consult a general physician first.
Q33. Do pills work immediately?
A. They are effective after 7 days of continuous use.
Q34. Can the pill cause diabetes?
A. It does not directly cause diabetes but may affect glucose tolerance in some women.
Q35. Do pills interact with antibiotics?
A. Some antibiotics may reduce effectiveness; ask your doctor.
Q36. Can I switch brands of pills easily?
A. Yes, but consult your doctor before switching.
Q37. Do pills affect hair growth?
A. They can reduce excess hair in some women with PCOS.
Q38. Can birth control pills cause nausea?
A. Yes, mild nausea is a common side effect.
Q39. Do pills reduce anemia?
A. Yes, by making periods lighter, they help prevent anemia.
Q40. Can I get birth control pills in any pharmacy?
A. Yes, they are widely available in pharmacies across India.
Q41. Do pills help regulate irregular cycles?
A. Yes, they are often prescribed for irregular periods.
Q42. Can I take pills during menopause?
A. They are usually stopped and replaced with hormone therapy if needed.
Q43. Do pills affect cholesterol?
A. Some types may slightly raise cholesterol levels.
Q44. Can I use the pill as emergency contraception?
A. No, specific emergency pills are designed for that purpose.
Q45. Do pills cause bloating?
A. Some women may feel bloated, especially in the first months.
Q46. Can I stop pills suddenly?
A. Yes, but your cycle may take time to adjust.
Q47. Do pills protect against endometrial cancer?
A. Yes, they reduce the risk significantly.
Q48. Can pills affect mental health?
A. Some women may experience mood changes, but effects vary.
Q49. Do birth control pills cause gallstones?
A. Rarely, they may increase the risk of gallbladder issues.
Q50. Should I see a general physician before starting pills?
A. Yes, always consult a doctor before beginning any hormonal contraceptive.
Quickobook Call-to-Action (CTA)
- Book an appointment with a general physician on Quickobook today.
- Find trusted pharmacies nearby for safe contraceptive pill purchases.
- Get online consultations for women’s health and contraception advice.
Disclaimer
This blog is for educational purposes only. It does not replace medical advice. Birth control pills should be taken only under the supervision of a qualified doctor. Always consult a general physician before starting, stopping, or switching contraceptives.





Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment