Introduction
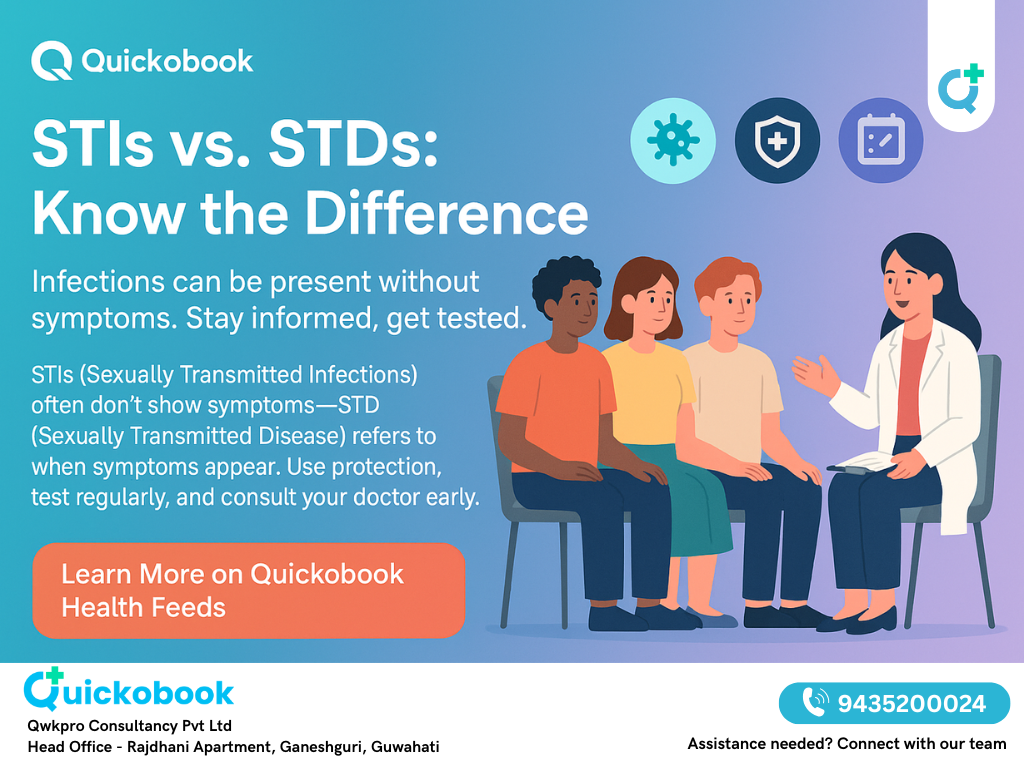
Sexual health is a cornerstone of overall wellness, yet in India, sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are often misunderstood. These terms are used interchangeably, but medically, they carry different meanings. The difference matters because early detection of STIs can prevent their progression into STDs like HIV-related AIDS. Lack of awareness, stigma, and myths worsen the burden of these conditions in India, where millions silently live with untreated infections.
This comprehensive Quickobook guide explains STIs vs. STDs, symptoms, risks, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies, with HIV as a key focus.
What Are STIs and STDs?
STIs – Sexually Transmitted Infections
- Refers to an infection caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites transmitted during sex.
- Often asymptomatic in early stages.
- Examples: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, HPV, HIV.
STDs – Sexually Transmitted Diseases
- Develop when an infection progresses and starts showing clinical symptoms or complications.
- Example: HIV infection develops into AIDS if untreated.
Key Point: All STDs begin as STIs, but not all STIs turn into STDs. Early treatment stops progression.
Common Causes of STIs & STDs
- Unprotected sex (vaginal, anal, oral).
- Multiple sexual partners without regular testing.
- Sharing needles (HIV, Hepatitis B/C).
- Mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Blood transfusions with untested blood (rare in regulated centers).
Symptoms
In Women
- Vaginal discharge (thick, foul-smelling).
- Burning sensation while urinating.
- Pelvic or abdominal pain.
- Irregular bleeding outside periods.
- Genital sores or warts.
In Men
- Penile discharge.
- Painful urination.
- Testicular pain.
- Blisters or ulcers on genitals.
General Symptoms (Both Sexes)
- Fever, swollen lymph nodes.
- Skin rashes.
- Weight loss and night sweats (advanced HIV/AIDS).
Note: Many STIs remain silent—especially HPV and chlamydia—making regular screening vital.
READ ALSO: A Guide To Excessive Porn And Mental Health: Science & Support
Diagnosis in India
- Blood tests: HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B/C.
- Urine tests: Chlamydia, gonorrhea.
- Swab cultures: Vaginal, penile, or throat swabs.
- Pap smear & HPV test: For cervical changes caused by HPV.
Cost in India: Basic STD panels cost ₹1,200–₹2,500. HIV testing starts from ₹300.
Treatment Options
- Bacterial STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis): Treated with antibiotics prescribed by a doctor.
- Viral STIs (HIV, herpes, HPV): No permanent cure, but antivirals and ART (antiretroviral therapy) manage infection.
- Parasitic infections (trichomoniasis): Cured with oral medicines.
Do not self-medicate. Treatment depends on infection type, stage, and overall health. Always consult a doctor.
Lifestyle & Prevention
- Use condoms consistently.
- Get vaccinated for HPV and Hepatitis B.
- Consider PrEP (Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis) if at high risk of HIV.
- Avoid alcohol/drugs that impair judgment.
- Test every 6–12 months if sexually active with multiple partners.
- Openly discuss sexual health with partners.
Risks & Complications
- Infertility (chlamydia, gonorrhea).
- Cervical cancer (HPV).
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- Pregnancy complications.
- HIV progressing to AIDS.
- Psychological stress due to stigma.
When to See a Doctor
- If you notice genital sores, unusual discharge, or painful urination.
- After unprotected sex with a new/multiple partners.
- If your partner has tested positive for an STI.
- For routine preventive check-ups, even without symptoms.
50 FAQs – STIs, STDs, and HIV
Q1. What is the difference between an STI and an STD?
A: An STI is an infection, often without symptoms. An STD is when the infection shows disease signs.
Q2. Is HIV the same as AIDS?
A: No. HIV is the virus, while AIDS is the advanced disease stage caused by untreated HIV.
Q3. Can STIs be asymptomatic?
A: Yes, infections like chlamydia and HPV may have no early symptoms.
Q4. Can STDs be cured?
A: Bacterial STDs can be cured with antibiotics. Viral ones like HIV can only be managed.
Q5. How soon after unprotected sex should I get tested?
A: Some STIs show up within 1–2 weeks, but HIV requires repeat testing after 3 months.
Q6. Can HIV spread through kissing?
A: No, unless there are open sores and blood contact.
Q7. How much does an HIV test cost in India?
A: Rapid tests start at around ₹300 in most labs.
Q8. Are condoms 100% effective?
A: No, but they significantly reduce risk of STIs including HIV.
Q9. Can oral sex transmit STIs?
A: Yes, infections like gonorrhea, herpes, and syphilis can spread.
Q10. Can STIs cause infertility?
A: Yes, untreated chlamydia or gonorrhea may lead to infertility.
Q11. Is HPV vaccination available in India?
A: Yes, for both men and women, starting from ₹2,500–₹3,000 per dose.
Q12. Can HIV be cured completely?
A: No, but ART controls the virus and ensures long survival.
Q13. Can washing after sex prevent STIs?
A: No, washing or douching does not prevent infections.
Q14. Can two HIV-negative partners have unprotected sex safely?
A: Yes, if both are recently tested and monogamous.
Q15. What is PEP?
A: Post-Exposure Prophylaxis is medicine taken within 72 hours of exposure to reduce HIV risk.
Q16. Is withdrawal a safe method to avoid STIs?
A: No, pre-ejaculate can carry both sperm and infections.
Q17. Can HIV spread by mosquito bites?
A: No, HIV cannot be transmitted by insects.
Q18. Do women show different STD symptoms than men?
A: Yes, women may have vaginal discharge, irregular bleeding, and pelvic pain.
Q19. Can syphilis be dangerous if untreated?
A: Yes, it may damage the heart, brain, and nerves.
Q20. How often should I get tested for STIs?
A: Every 6–12 months if you are sexually active with multiple partners.
Q21. What are the first signs of HIV?
A: Fever, rash, swollen glands, and flu-like symptoms in early weeks.
Q22. Is HIV always fatal?
A: No, with ART, HIV-positive people can live normal lifespans.
Q23. Can pregnant women pass STDs to their babies?
A: Yes, during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding.
Q24. Is self-testing for HIV reliable?
A: Yes, but confirm with lab tests for accuracy.
Q25. Can alcohol increase STD risk?
A: Yes, it lowers judgment and leads to unsafe sex.
Q26. Can genital herpes be cured?
A: No, but antiviral drugs reduce outbreaks.
Q27. Can HIV be transmitted through blood donation?
A: No, donated blood is screened before transfusion in India.
Q28. Can you catch STIs from a toilet seat?
A: No, STIs do not spread this way.
Q29. Do men need HPV vaccine?
A: Yes, it prevents genital warts and cancers.
Q30. What is the incubation period of HIV?
A: HIV may remain symptomless for years before progressing.
Q31. Can STDs cause cancer?
A: Yes, HPV can lead to cervical, anal, and throat cancers.
Q32. Is it safe to breastfeed if HIV-positive?
A: Doctors advise caution; ART reduces risk but does not eliminate it.
Q33. Can untreated gonorrhea spread in the body?
A: Yes, it can affect joints and organs.
Q34. Can one-time unprotected sex cause HIV?
A: Yes, even one encounter can transmit HIV.
Q35. Are STIs common in India?
A: Yes, but many cases go unreported due to stigma.
Q36. Do condoms protect against HPV?
A: Partially, as HPV spreads via skin-to-skin contact.
Q37. Can men show no symptoms of STIs?
A: Yes, many men remain asymptomatic but infectious.
Q38. What are the stages of syphilis?
A: Primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary.
Q39. Can HIV be transmitted through saliva?
A: No, unless blood is present in large amounts.
Q40. What is ART for HIV?
A: Antiretroviral therapy, a lifelong medicine regimen controlling HIV.
Q41. Can STIs cause pregnancy complications?
A: Yes, infections can cause miscarriage or preterm birth.
Q42. Do home remedies cure STDs?
A: No, medical treatment is essential.
Q43. Can men with HIV father children safely?
A: Yes, with proper treatment and medical planning.
Q44. How accurate are HIV rapid tests?
A: Around 99% if done after the window period.
Q45. Can syphilis be detected in a blood test?
A: Yes, with VDRL and other specific tests.
Q46. Can untreated HIV affect mental health?
A: Yes, it may lead to depression and neurological issues.
Q47. Can condoms break during sex?
A: Rarely, but proper use reduces risk.
Q48. Are STDs covered in insurance in India?
A: Some plans cover testing and treatment; check policy terms.
Q49. Can one have more than one STI at once?
A: Yes, co-infections are common.
Q50. Where can I book a confidential STD test in India?
A: Quickobook lets you book private, reliable tests and doctor consultations online.
Conclusion
The difference between STIs and STDs is crucial: infections may be silent, but untreated they progress into diseases with severe consequences like HIV/AIDS, infertility, and cancers. Prevention, regular testing, and early treatment are your strongest shields. With Quickobook, you can access confidential tests, professional consultations, and trusted care in your city.
Quickobook CTAs
- Book a confidential STD/HIV test through Quickobook today.
- Consult a qualified general physician or specialist online/offline.
- Get reminders for regular health check-ups and preventive vaccines.
Disclaimer: This blog is for educational purposes only. It does not replace medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor for diagnosis and treatment.





Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment